- Climate change is changing Arctic ecosystems. It’s shifting food sources from plants to decayed matter because the ice is melting and it’s getting hotter.
- Changes in temperature affect how energy moves in ecosystems, altering the diet of small mammals. Even though this changes things, they mostly eat new carbon, not old carbon from thawing permafrost.
- Understanding these changes is really important for predicting how the climate will react. We need more research and everyone working together to protect these sensitive places.
High-latitude ecosystems, particularly in the Arctic tundra and boreal forests, face significant upheavals due to climate change. Recent research, published in Nature Climate Change, delves into the repercussions of these changes on food webs, shedding light on the transformation of these delicate ecosystems.
The study, spearheaded by Philip Manlick and a team from various esteemed institutions, highlights the profound alterations in food webs, affecting animals acclimatized to extreme cold conditions. As temperatures rise, permafrost melts, triggering a surge in microbial activity that reshapes the ecosystems. Previously sustained by “green” plant-based food webs, small mammals like shrews and voles now predominantly rely on “brown” fungal food webs.
Tracking Climate Change Over Time: Insights from Museum Specimens
The study covers 30 years of looking at what small mammals eat from the 1990s until now. It also looks at Arctic wolf spiders that were warmed up in experiments. They used special analysis on museum samples to see how energy moves through food chains. They found that warming consistently changes energy flow in ecosystems, making them more “brown.”
Even though ecosystems become more “brown,” animals mostly eat new carbon instead of old carbon from thawing permafrost. This shows how climate change affects these ecosystems in complicated ways.
Unraveling the Mystery: The Rise of “Brown” Food Webs
While the surge in “brown” food webs indicates a significant shift, the source supporting fungal growth remains enigmatic. Speculations initially pointed towards ancient permafrost; however, radiocarbon data challenges this assumption. The dynamics of permafrost carbon cycling are intricate, suggesting alternative mechanisms like increased decomposition of new plant growth.
Implications and Future Directions
Understanding these nuanced changes is pivotal for predicting ecosystem responses to climate change. As these sensitive environments undergo rapid transformations, this research lays the groundwork for future studies, highlighting the relevance of museum specimens in comprehending temperature change effects.
Importance of Arctic’s Microscopic Ecosystem: Impact of Climate Shifts
Climate Shifts and Implications on the Food Web
In the Arctic, big changes in the atmosphere are happening fast. This is causing really important changes in the oceans there. The ice is melting, and the temperatures are going up, which is having a big impact on the tiny creatures that are vital for the food chain. It shows how everything in the Arctic is connected.
Phytoplankton’s Vital Role in Ecosystem Stability
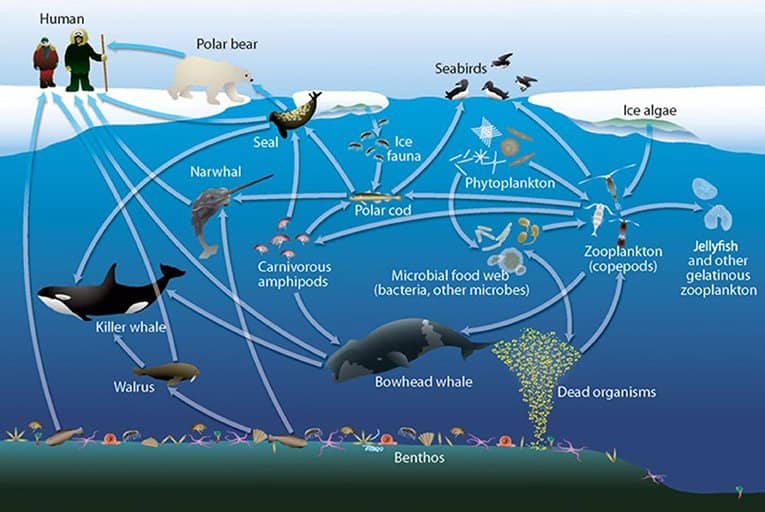
Tiny plants in the ocean, called phytoplankton, are super important. They make a lot of oxygen and help store carbon. Some of these tiny plants, called diatoms, live in sea ice and are really important for keeping life going in the Arctic.
Zooplankton: Connecting the Dots in the Food Web
Zooplankton are like the middlemen between phytoplankton and bigger predators. They’re really important because they spread around essential nutrients. Diatoms, a big meal for zooplankton, play a key role in keeping the Arctic’s diverse ecosystem going. They help out creatures like polar cod, seabirds, and whales.
Vulnerabilities and Adaptations Amidst Changing Conditions
Changes in the Arctic throughout the seasons, especially in dark winter, are tough for plant-eating animals and small creatures called copepods that depend on plants. They have to adapt and change how they eat a lot when there are a ton of tiny plant-like organisms around. This is super important for them to live through this time because it impacts how they make babies and store energy.
Future Projections and the Need for Collective Action
The decrease in tiny ocean plants and changes in the Arctic are big problems. They threaten bigger animals and people who depend on these food systems. To fix this, we need everyone to work together, be aware, and support projects like the Changing Arctic Ocean program. This will help reduce the harm and promote better ways of doing things.
Conclusion
The Arctic is experiencing unprecedented changes, making it crucial to understand the intricate web of life in these ecosystems. Research into these areas sheds light on how climate change affects food webs. It underscores the urgency of taking proactive measures and conducting more research to protect these fragile environments.