- Scientists created a 17-step process in E. coli that turns CO2 into Acetyl-CoA, a crucial cell component.
- Using this cycle in E. coli shows synthetic biology progress, but aligning it with the cell’s complex metabolism poses challenges.
- This innovation enables new pathways to convert CO2 into valuable compounds, with uses in biotechnology and fighting climate change.
Table of Contents
Synthetic biology provides a chance to create biochemical pathways that capture and convert carbon dioxide (CO2). At the Max-Planck-Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology, researchers have designed a synthetic biochemical cycle that converts CO2 into Acetyl-CoA, the central building block.
The successful implementation of all three cycle modules in the bacterium E. coli by the researchers is a significant advancement towards the realization of synthetic CO2 fixing routes in the context of living cells.
Addressing the climate problem requires creating innovative methods for capturing and converting CO2. Through synthetic biology, it is possible to create CO2-fixation pathways that are not found in nature and that trap CO2 more effectively.
Realizing those novel pathways in many in vitro and in vivo settings remains a basic difficulty.
The THETA Cycle: A Novel CO2-Fixation Process
Recently, scientists working with Tobias Erb’s group have created the so-called THETA cycle, a novel synthetic CO2-fixation process.
The two quickest CO2-fixing enzymes currently known to science, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and crotonyl-CoA carboxylase/reductase, were the basis for the complete THETA cycle, which entailed 17 biocatalysts.
These potent biocatalysts were discovered by the researchers in bacteria. Despite the fact that RubisCO, the CO2-fixing enzyme found in chloroplasts, can capture CO2 more than ten times faster than any other carboxylase, evolution has not managed to bring these two highly powerful enzymes together for natural photosynthesis.
In a single cycle, the THETA cycle transforms two CO2 molecules into one acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is an important metabolite in practically all cellular metabolism and the basis for several essential biomolecules, such as medicines, biofuels, and biomaterials. For these reasons, it is a chemical of great interest in biotechnological applications. The cycle’s operation could be verified by the researchers once they assembled it in test tubes.
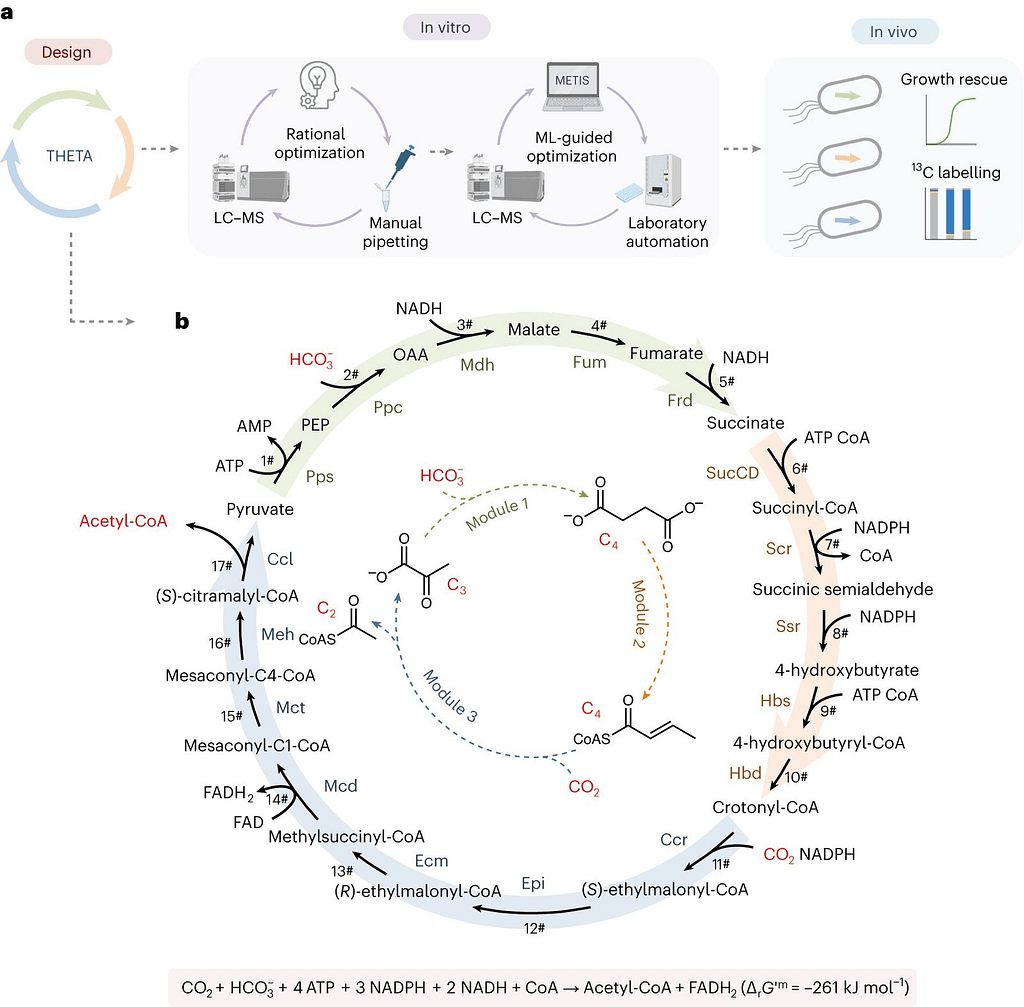
The training process then started, and after multiple iterations of experiments, the team was able to increase the acetyl-CoA yield by a factor of 100 through optimization led by machine learning and reasoning. Step-by-step integration into the living cell is necessary to verify its viability in vivo.
In order to achieve this, the scientists separated the THETA cycle into three modules, each of which was added to the E. coli bacteria with success. These modules’ functionality was confirmed by isotope tagging and/or growth-coupled selection.
This cycle is unique since it includes a number of intermediates that are important metabolites in the metabolism of the bacteria. The study’s principal author, Shanshan Luo, says, “This overlap offers the opportunity to develop a modular approach for its implementation.”
Challenges and Future Prospects in Metabolic Pathway Integration
“We demonstrated the efficacy of each of the three individual components in E. coli. Nevertheless, she continues, “We still haven’t been able to shut down the entire cycle so that E. coli can grow only on CO2. Since all 17 reactions must be coordinated with the hundreds to thousands of events that comprise E. coli’s normal metabolism, closing the THETA cycle remains a difficult task.
Nevertheless, the researcher highlights other objectives in addition to exhibiting the entire cycle in vivo. “Our cycle has the potential to become a versatile platform for producing valuable compounds directly from CO2 through extending its output molecule, acetyl-CoA,” claims Shanshan Luo.
Tobias Erb says, “Introducing sections of the THETA cycle into living cells is a crucial demonstration for synthetic biology.” This cycle’s modular application in E. coli opens the door to the development of extremely intricate, orthogonal, novel CO2-fixation pathways in cell factories. To build a synthetic autotrophic operating system for the cell, we are discovering how to entirely rewire the metabolism of the cell.”
This cycle’s modular application in E. coli opens the door to the development of extremely intricate, orthogonal, novel CO2-fixation pathways in cell factories. To build a synthetic autotrophic operating system for the cell, we are discovering how to entirely rewire the metabolism of the cell.”
The research has been published in the Nature Catalysis journal.
![[Downloader.la]-659593f8e8b71 Two bioreactors filled with green algae fixing CO2 to help reduce climate change, Arcos de la Frontera, Cadiz, Costa de la Luz, Andalusia, Spain.](https://mla9xb2ybyum.i.optimole.com/w:696/h:464/q:mauto/f:best/https://dailywestnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Downloader.la-659593f8e8b71.jpg)
